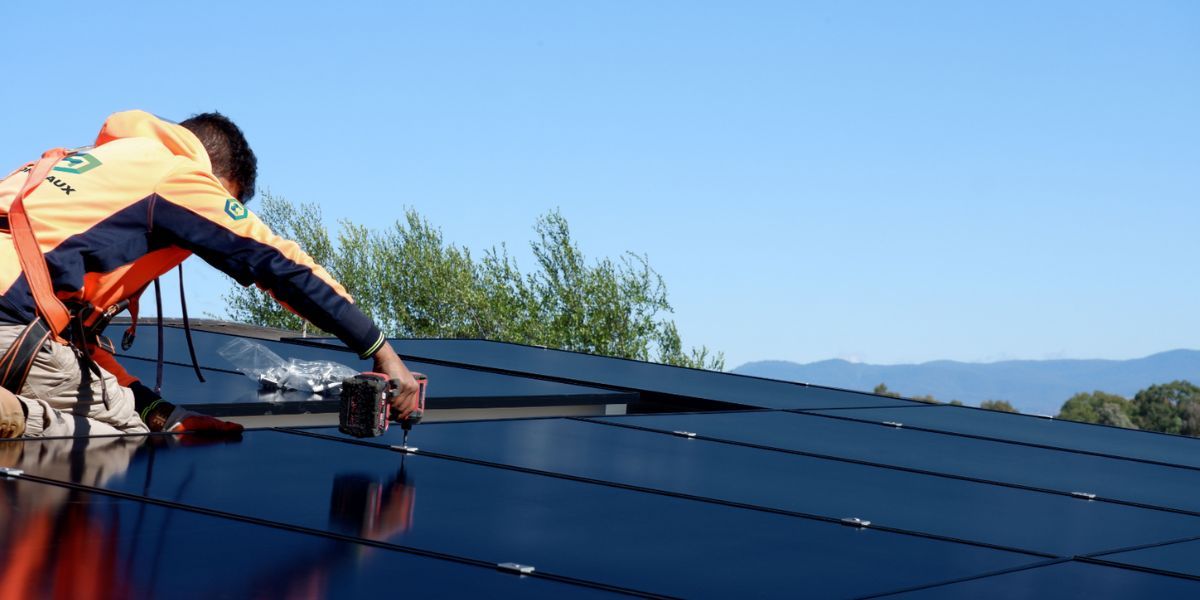
Solar Batteries Functions
If you are thinking about adding a battery storage system and wondering if it is worth adding, read this article to help you find out the possible functions of a battery storage system for grid-connected PV systems. In short, batteries serve two purposes: increase self-consumption, and provide backup when the grid is not working (it is optional, the cost of battery backup varies depending on the battery).
1. Maximise self-consumption
Maximising self-consumption also means minimising PV export. The system charges its batteries from excess PV production. The stored energy can be discharged whenever desired. This function would be desirable if there are network limitations or if PV export attracts very little feed-in tariff.
2.Tariff arbitrage
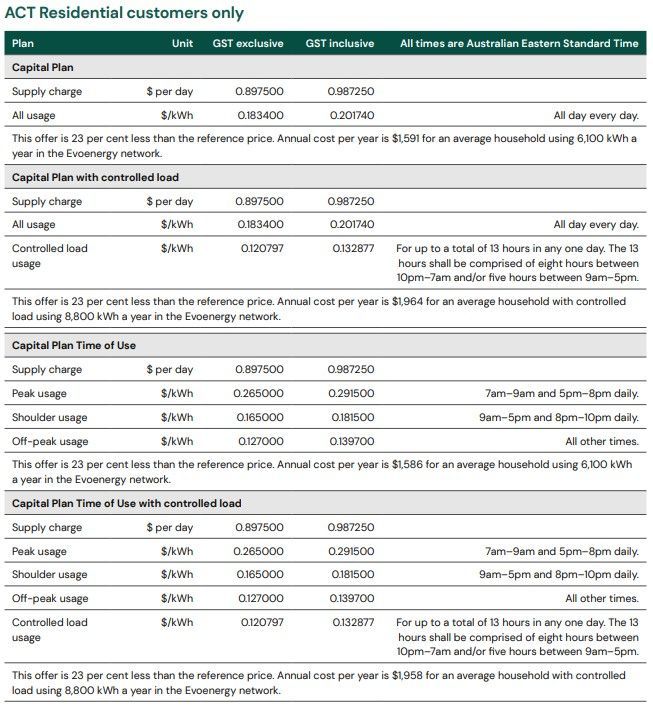
The function only applies for the house with time of use tariff. In the mode of time of use, it charges customers different electricity rates depending on the time of day. In the example of ActewAGL, energy usage at peak times are from 7am-9am and 5pm-8pm everyday, shoulder times are from 9am-5pm and from 8pm-10pm everyday, off-peak times are the usage at all other times.
3.Grid back up
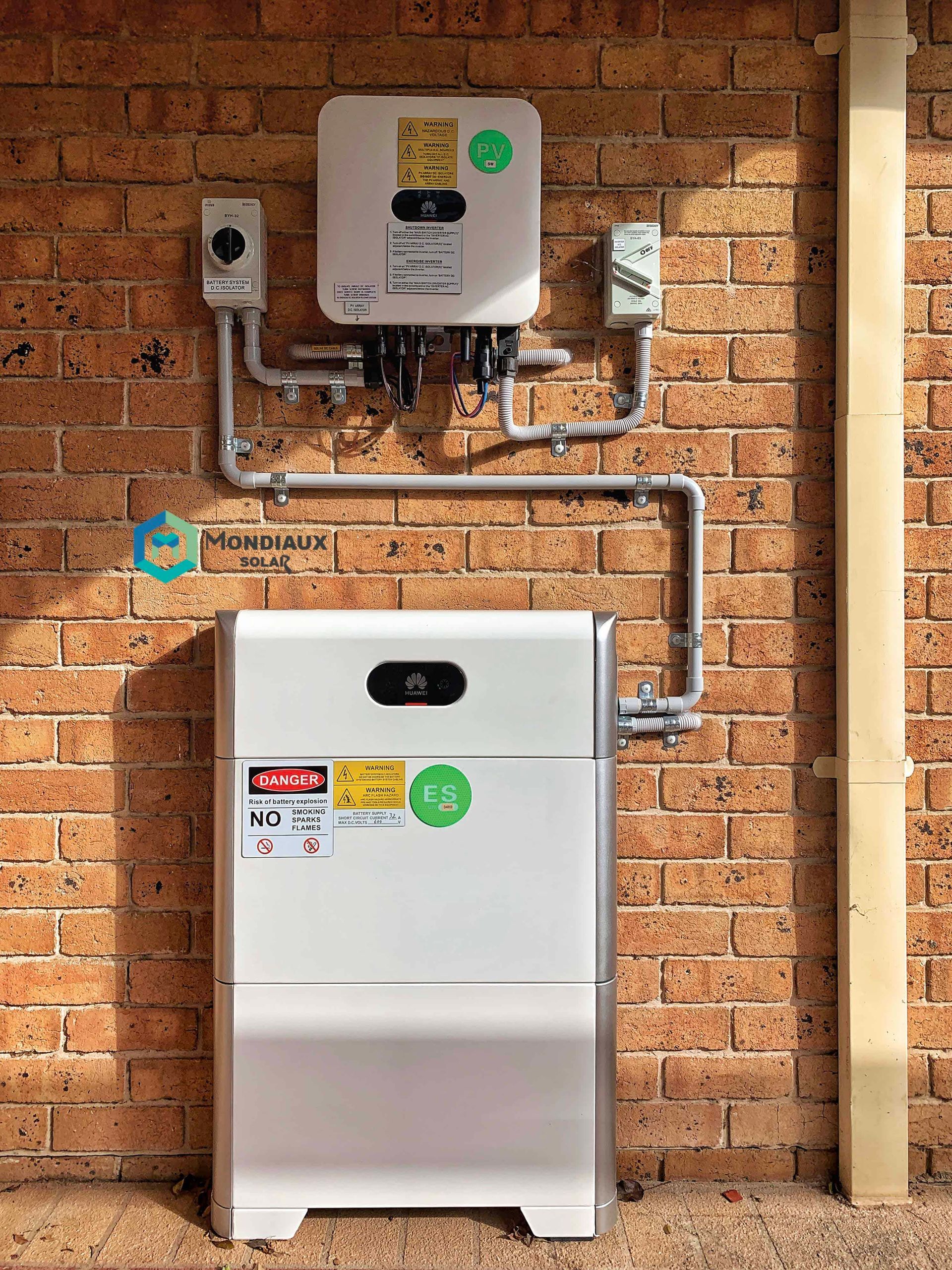
If you live in a rural area where the electrical grid is unreliable or extreme weather events are common in your area, the function here is most useful. In the event of blackout, battery system provides an alternate supply for some or all of your house’s loads. This is also known as emergency power supply (EPS). The function is available for DC-coupled batteries from Huawei, Alpha and Sungrow, or Tesla (AC coupled battery with solar).
Share Post